The Importance of Ear Cytology in Veterinary Medicine

Ear cytology is a vital diagnostic tool in veterinary medicine, providing critical insights into ear health, diagnosing infections, and guiding treatment. Given the frequency of ear problems in dogs and cats, performing an ear cytology is an essential part of managing diseases of the ear.
Understanding Ear Cytology
Ear cytology involves collecting a sample from the ear canal, typically through a cotton swab, and examining it under a microscope. This test identifies the presence of organisms such as bacteria, yeast, or parasites, as well as inflammatory cells. It is a non-invasive, quick, and cost-effective procedure that can be performed in-clinic.
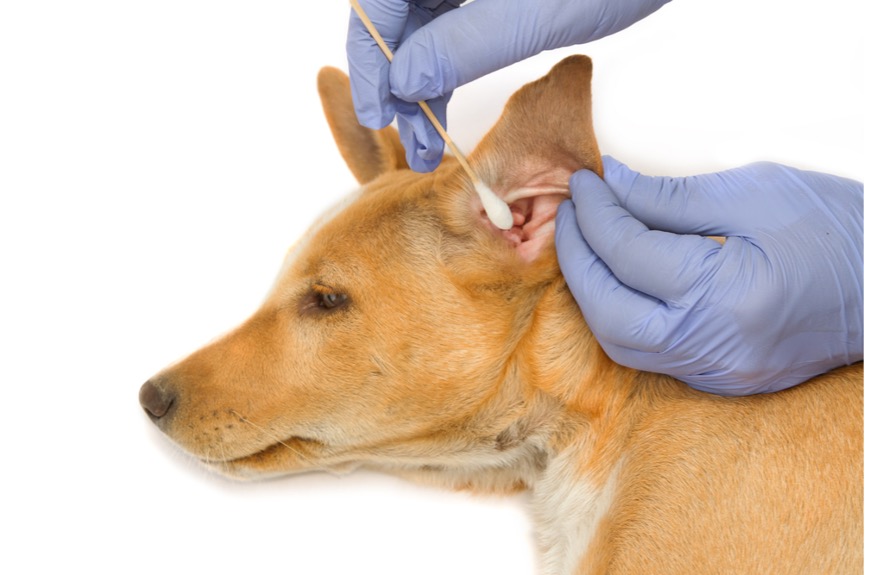
Why Ear Cytology is Necessary
- Diagnosing Ear Infections: Otitis externa, or ear infections, is one of the most common reasons for veterinary visits, especially in dogs. These infections can be caused by a range of factors including bacteria, yeast, parasites (like ear mites), allergies, or foreign bodies.
By using ear cytology, veterinarians can determine the exact cause of the infection, allowing for targeted treatment. For instance, an infection caused by yeast requires antifungal therapy, while bacterial infections need antibiotics. Without cytology, treatment might be generalized and less effective. - Guiding Effective Treatment: Knowing the specific organisms involved in an ear infection helps us prescribe the most appropriate medications. Ear cytology helps in differentiating between bacterial and fungal infections, enabling a tailored treatment approach. This reduces the risk of treatment failure and ensures a quicker recovery for patients. Moreover, it helps in deciding if a topical or systemic treatment is required, which reduces unnecessary use of medications that might have side effects.
- Monitoring Treatment Progress: After initiating treatment, repeat ear cytologies are often necessary to assess the effectiveness of the therapy. Some infections may be resistant to treatment, or secondary infections may develop, requiring a change in medication. Monitoring with ear cytology ensures that the treatment is working and that any complications are identified early.
- Detecting Underlying Conditions: Chronic or recurrent ear infections often indicate underlying conditions such as allergies, endocrine disorders, or autoimmune diseases. Ear cytology helps in identifying whether an infection is truly recurrent or if the initial infection was never fully resolved. This also highlights the need for further diagnostic workups to address the primary cause.
- Preventing Chronic Ear Disease Chronic ear infections can lead to long-term damage, such as thickening of the ear canal, scarring, or even hearing loss. Identifying and treating infections early through ear cytology helps prevent these complications. In severe cases, untreated chronic infections can lead to the need for surgical intervention, such as total ear canal ablation (TECA). Early cytological diagnosis and treatment can prevent the need for such drastic measures.
